Discovering Kidney Stones vs UTI: A Clear Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Remedies
Discovering Kidney Stones vs UTI: A Clear Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Remedies
Blog Article
An In-Depth Analysis of Therapy Alternatives for Kidney Stones Versus Urinary Tract Infections: What You Need to Know
The difference in between treatment alternatives for kidney stones and urinary system tract infections (UTIs) is critical for efficient individual administration. While UTIs are normally attended to with antibiotics that give quick alleviation, the approach to kidney stones can vary dramatically based on private variables such as stone size and composition. Non-invasive approaches like extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) might appropriate for smaller sized stones, yet bigger or obstructive stones usually require more intrusive techniques. Recognizing these nuances not only educates medical choices however additionally enhances person end results, welcoming a more detailed examination of each condition's therapy landscape.
Recognizing Kidney stones
Kidney stones are hard down payments created in the kidneys from minerals and salts, and recognizing their structure and development is crucial for reliable monitoring. The primary kinds of kidney stones include calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, struvite, uric acid, and cystine stones, each with distinctive biochemical beginnings.
The development of kidney stones happens when the concentration of certain substances in the urine raises, resulting in condensation. This condensation can be influenced by urinary system pH, volume, and the existence of preventions or promoters of stone formation. Low pee volume and high level of acidity are conducive to uric acid stone development.
Recognizing these variables is vital for both prevention and treatment (Kidney Stones vs UTI). Efficient administration methods may consist of dietary adjustments, increased liquid intake, and, in some instances, pharmacological treatments. By identifying the underlying causes and types of kidney stones, doctor can apply customized methods to minimize reappearance and boost client end results
Summary of Urinary System Infections
Urinary system infections (UTIs) prevail bacterial infections that can influence any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most of UTIs are created by Escherichia coli (E. coli), a sort of microorganisms generally found in the intestinal tracts. Ladies are more vulnerable to UTIs than men as a result of physiological distinctions, with a much shorter urethra helping with less complicated microbial access to the bladder.
Symptoms of UTIs can differ depending on the infection's area but frequently consist of constant peeing, a burning sensation during urination, strong-smelling or cloudy urine, and pelvic pain. In much more severe cases, especially when the kidneys are involved, signs may additionally include high temperature, cools, and flank discomfort.
Threat factors for creating UTIs consist of sex, particular sorts of contraception, urinary system abnormalities, and a damaged body immune system. Diagnosis typically includes pee tests to recognize the existence of bacteria and various other signs of infection. Trigger therapy is important to protect against complications, consisting of kidney damages, and generally involves anti-biotics tailored to the particular germs entailed. UTIs, while common, call for timely acknowledgment and administration to make sure effective end results.
Treatment Choices for Kidney stones
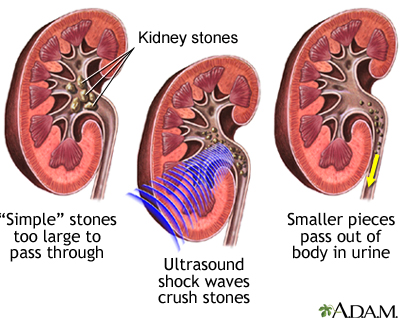
If the stones are larger or trigger substantial discomfort, non-invasive treatments such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) may be used. This technique uses audio waves to damage the stones right into smaller sized fragments that can be much more conveniently gone through the urinary system tract.
In instances where stones are too huge for ESWL or if they obstruct the urinary tract, ureteroscopy might be shown. This minimally invasive treatment entails using a tiny extent to damage or eliminate up the stones straight.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-GettyImages-1391949232-d78548898e2e4ef2b88ac7c5f2a93436.jpg)
Therapy Options for UTIs
How can healthcare service providers efficiently resolve urinary system tract infections (UTIs)? The main approach entails a comprehensive evaluation of the individual's signs and case history, adhered to by suitable diagnostic screening, such as urinalysis and pee society. These examinations assist recognize the original virus and establish their antibiotic susceptibility, assisting targeted treatment.
First-line treatment typically consists of antibiotics, with choices such as nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, relying on local resistance patterns. For straightforward instances, a brief training course of prescription antibiotics (3-7 days) is frequently enough. In persistent UTIs, providers might take into consideration preventative anti-biotics or different techniques, consisting of way of living adjustments to reduce threat factors.
For clients with complex UTIs or those with underlying health and wellness concerns, more aggressive treatment might be necessary, potentially entailing intravenous antibiotics and additional diagnostic imaging to analyze for issues. Furthermore, client education on hydration, hygiene practices, and symptom monitoring plays a critical duty in avoidance and reoccurrence.
Contrasting Outcomes and Performance
Assessing the results and efficiency of treatment options for urinary system infections (UTIs) is important for maximizing patient care. The main treatment for straightforward UTIs normally investigate this site involves antibiotic therapy, with options such as nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and fosfomycin.
In comparison, treatment end results for kidney stones differ significantly based on stone composition, dimension, and area. Choices range from traditional management, such as hydration and discomfort control, to interventional procedures like extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) and ureteroscopy. While ESWL has a high success rate for smaller sized stones, difficulties can arise, demanding more treatments.
Ultimately, the efficiency of therapies for both conditions depends upon exact medical diagnosis and tailored approaches. While UTIs usually respond well to anti-biotics, kidney stone management might call for a multifaceted strategy. Continuous evaluation of therapy end results is important to boost individual experiences and decrease reoccurrence prices for both UTIs and kidney stones.
Conclusion
In recap, treatment strategies for kidney stones and urinary system tract infections differ substantially due click here to find out more to the unique visit our website nature of each problem. Non-invasive approaches such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy are appropriate for smaller stones, whereas larger or obstructive stones might need ureteroscopy.
While UTIs are generally addressed with antibiotics that provide rapid alleviation, the approach to kidney stones can vary significantly based on private factors such as stone size and structure. Non-invasive techniques like extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) might be suitable for smaller sized stones, yet larger or obstructive stones commonly need even more invasive strategies. The key kinds of kidney stones consist of calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, struvite, uric acid, and cystine stones, each with distinct biochemical beginnings.In contrast, treatment results for kidney stones differ substantially based on stone structure, dimension, and place. Non-invasive approaches such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy are suitable for smaller stones, whereas larger or obstructive stones might require ureteroscopy.
Report this page